Empowering Energy Networks: LiDAR's Role in Transmission and Distribution
In the ever-evolving landscape of energy transmission and distribution, technology is paving the way for more efficient, reliable, and sustainable systems. Among the cutting-edge tools that have emerged, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology stands out as a crucial instrument, revolutionizing the way power utilities manage their infrastructure.
LiDAR in Transmission and Distribution:
LiDAR, a remote sensing technology that employs laser beams to measure distances and create detailed 3D models, has found a pivotal role in the energy sector. In the context of transmission and distribution, LiDAR offers utilities an accurate and comprehensive understanding of their infrastructure's conditions, enabling smarter decision-making and more effective maintenance strategies.
Applications in Transmission and Distribution:
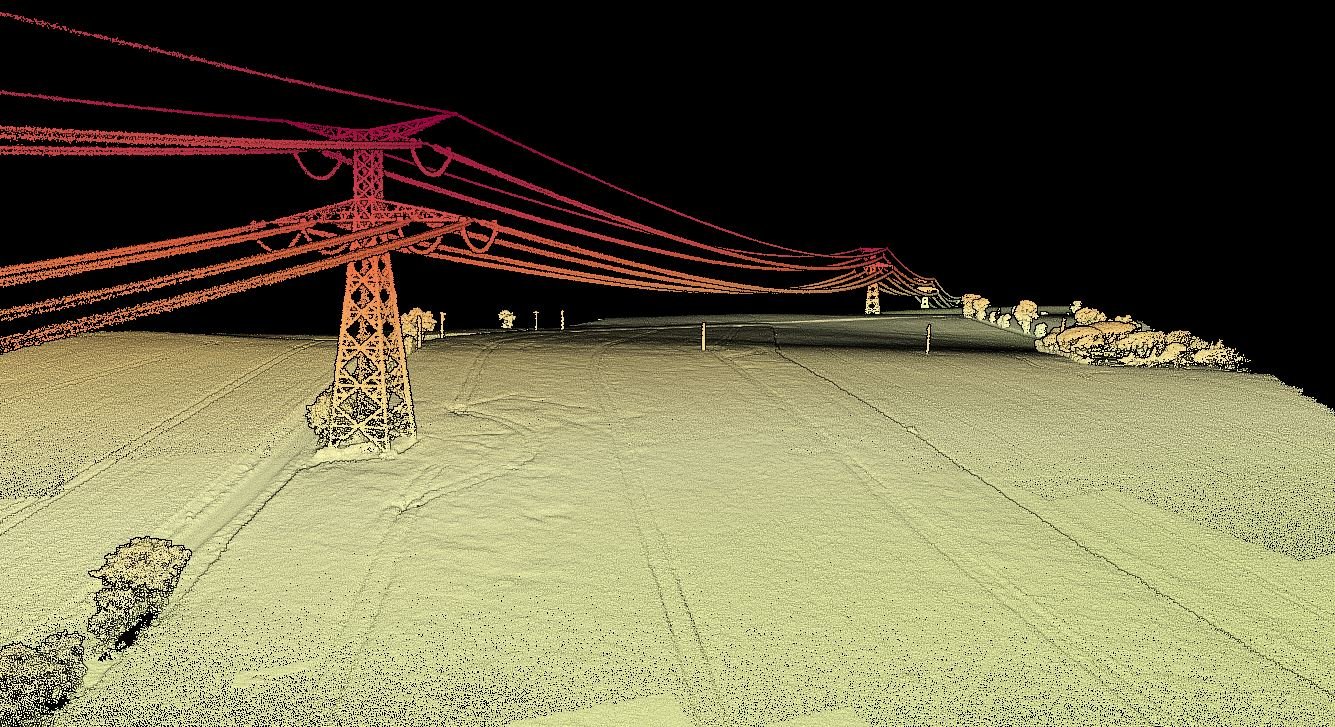
Vegetation Management: Overgrown vegetation is a common challenge in power distribution and transmission lines. LiDAR scans provide utilities with detailed information about the proximity of trees and vegetation to power lines, enabling proactive vegetation management and reducing the risk of outages caused by tree-related incidents.
Asset Inventory and Management: LiDAR technology facilitates rapid and accurate asset inventory by capturing detailed data on transmission towers, poles, conductors, and other components. This information aids utilities in tracking the condition of assets, identifying potential issues, and planning for maintenance or replacement.
Inspection and Maintenance: Traditional inspection methods for power infrastructure can be time-consuming and hazardous. LiDAR-equipped drones can perform aerial inspections, capturing high-resolution images and 3D models of power lines and substations. This data enhances maintenance planning and reduces the need for manual inspections in dangerous environments.
Terrain Analysis and Line Siting: LiDAR-generated topographical data assists utilities in selecting optimal routes for new transmission and distribution lines. By analyzing elevation changes, obstacles, and environmental factors, utilities can minimize construction challenges and environmental impacts.
Disaster Response and Recovery: In the aftermath of natural disasters, LiDAR technology aids utilities in assessing the extent of damage to their infrastructure. Rapid deployment of LiDAR-equipped drones provides real-time data that guides restoration efforts and expedites recovery.
Efficiency, Safety, and Sustainability:
The incorporation of LiDAR technology into transmission and distribution processes offers several significant benefits. First and foremost, it enhances operational efficiency by providing utilities with accurate data, reducing the need for manual inspections and optimizing maintenance schedules. This efficiency translates into minimized downtime and improved service reliability.
Furthermore, LiDAR's ability to capture detailed 3D models from a safe distance contributes to enhanced worker safety. Drones equipped with LiDAR can perform inspections in challenging or hazardous environments without putting human personnel at risk.
From a sustainability perspective, LiDAR plays a vital role in reducing the environmental impact of energy infrastructure. Optimal line siting based on accurate topographical data reduces the need for extensive land clearing and minimizes disruption to ecosystems.
LiDAR's integration into the transmission and distribution sector is transforming the way power utilities operate and manage their networks. Its capacity to provide accurate, real-time data empowers utilities to make informed decisions, enhance operational efficiency, and ensure the reliability of energy supply. As the energy industry continues to navigate the path towards a sustainable and technologically advanced future, LiDAR's role in transmission and distribution becomes an indispensable asset, contributing to a smarter, safer, and more resilient power infrastructure.